The profile is the location where all data about a user are stored, including the user’s environment and preference settings. For example when you install a software (i.e. Outlook) the configuration and data about this user (account, database of all the emails) are stored in user profile (default configuration). If another user logon in the same PC, with another account, this user won’t see the data and configuration/personalization of the former user: every users has a different profile (i.e. this user won’t see the account used by the former user, and the emails too).
Yearly Archives: 2012
Connect Php code in Linux to Ms Sql Server using Freetds
Using Freetds we can connect php code in Linux to Microsoft Sql Server.
We start from a fresh installation of Ubuntu 11.04.
# apt-get install dpkg-dev # apt-get install apache2 # apt-get install php5 # /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
To check that php5 works fine
# php -v PHP 5.3.5-1ubuntu7.10 with Suhosin-Patch (cli) (built: Jun 19 2012 00:54:05) Copyright (c) 1997-2009 The PHP Group Zend Engine v2.3.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2010 Zend Technologies
Now if all works fine you can continue. Click here to continue reading Php code in Linux to Ms Sql Server using Freetds
How to remove trojan Windows Active Guard
In the next the procedure on how to remove the trojan Windows Active Guard.
From SIP to RTP (Part 6) – The phone is ringing….
Real Case: Asterisk receive an external call
A call from an external number to our pbx using a SIP trunk.
Att: I have “sniffed” that traffic using tcpdump.
tcpdump -i <interface> -s 65535 -w <file name>
In the next the Asterisk pbx is inside a LAN network, and its ip address is 10.10.10.110. The router in the network is configured with a public ip address 79.14.212.52. Asterisk is configured correctly using local network & public network parameters: in this mode all the message in SIP will be correctly valuated.
File sip.conf
[general] externip = 79.14.212.52 localnet=10.10.10.0/255.255.255.0
>>Message from ISTP provider (IP 212.97.59.76) to Pbx (ip: 10.10.10.110)
INVITE sip:5224851@79.14.212.52 SIP/2.0 Record-Route: <sip:212.97.59.76:5061;lr=on;ftag=as16df4853;rpp=np> Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.76:5061;branch=z9hG4bKc7f1.f1fb7516.1 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.85:5060;branch=z9hG4bK683ee34f;rport=5060 From: "+393461050897" <sip:+393461050897@sip.messagenet.it>;tag=as16df4853 To: <sip:01042064023@212.97.59.76:5061> Contact: <sip:+393461050897@212.97.59.85> Call-ID: 509017dd3847bf900f839d877abfd752@sip.messagenet.it CSeq: 102 INVITE User-Agent: foxtrot Max-Forwards: 69 Date: Tue, 29 Nov 2011 00:29:39 GMT Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO Supported: replaces Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 356 v=0 o=root 21598 21598 IN IP4 193.227.104.40 s=session c=IN IP4 193.227.104.40 t=0 0 m=audio 35936 RTP/AVP 18 3 97 8 0 101 a=rtpmap:18 G729/8000 a=fmtp:18 annexb=no a=rtpmap:3 GSM/8000 a=rtpmap:97 iLBC/8000 a=fmtp:97 mode=30 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:101 0-16 a=ptime:20 a=sendrecv
The trace show an incoming call from number +393461050897 to our number (trunk with ITSP) that is 01042064023.
Att.: 5224851 is another internal number assigned from ITSP to the trunk that is linked to 01042064023: very commonly the ITSP use this “internal number” for REGISTER & OPTIONS messages.
Att.: The ITSP know where is located the our pbx because Asterisk send periodically a REGISTER & OPTIONS messages: the NAT is “opened” by this kind of messages.
The ITSP wants to receive the voice streaming to 193.227.104.40 port 35936.
Att: Very interesting the UA that receive the voice stream is different from the UA that establish the call (different ip address): it is very common using big ITSP.
>> Messages from PBX (ip 10.10.10.110) to ISTP provider (IP 212.97.59.76).
SIP/2.0 100 Trying Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.76:5061;branch=z9hG4bKc7f1.f1fb7516.1;received=212.97.59.76 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.85:5060;branch=z9hG4bK683ee34f;rport=5060 Record-Route: <sip:212.97.59.76:5061;lr=on;ftag=as16df4853;rpp=np> From: "+393461050897" <sip:+393461050897@sip.messagenet.it>;tag=as16df4853 To: <sip:01042064023@212.97.59.76:5061> Call-ID: 509017dd3847bf900f839d877abfd752@sip.messagenet.it CSeq: 102 INVITE User-Agent: FPBX-2.8.1(1.4.40) Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO Supported: replaces Contact: <sip:5224851@79.14.212.52> Content-Length: 0
>> Messages from PBX (ip 10.10.10.110) to ISTP provider (IP 212.97.59.76).
SIP/2.0 200 OK Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.76:5061;branch=z9hG4bKc7f1.f1fb7516.1;received=212.97.59.76 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.85:5060;branch=z9hG4bK683ee34f;rport=5060 Record-Route: <sip:212.97.59.76:5061;lr=on;ftag=as16df4853;rpp=np> From: "+393461050897" <sip:+393461050897@sip.messagenet.it>;tag=as16df4853 To: <sip:01042064023@212.97.59.76:5061>;tag=as5dfb4137 Call-ID: 509017dd3847bf900f839d877abfd752@sip.messagenet.it CSeq: 102 INVITE User-Agent: FPBX-2.8.1(1.4.40) Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO Supported: replaces Contact: <sip:5224851@79.14.212.52> Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 238 v=0 o=root 2754 2754 IN IP4 79.14.212.52 s=session c=IN IP4 79.14.212.52 t=0 0 m=audio 18480 RTP/AVP 8 101 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:101 0-16 a=silenceSupp:off - - - - a=ptime:20 a=sendrecv
>>Final ACK
ACK sip:5224851@79.14.212.52 SIP/2.0 Record-Route: <sip:212.97.59.76:5061;lr=on;ftag=as16df4853> Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.76:5061;branch=0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 212.97.59.85:5060;branch=z9hG4bK0bbcf9cd;rport=5060 From: "+393461050897" <sip:+393461050897@sip.messagenet.it>;tag=as16df4853 To: <sip:01042064023@212.97.59.76:5061>;tag=as5dfb4137 Contact: <sip:+393461050897@212.97.59.85> Call-ID: 509017dd3847bf900f839d877abfd752@sip.messagenet.it CSeq: 102 ACK User-Agent: foxtrot Max-Forwards: 69 Content-Length: 0
Asterisk accepts the call and declare that want to receive voice stream to 79.14.212.52 port 18480.
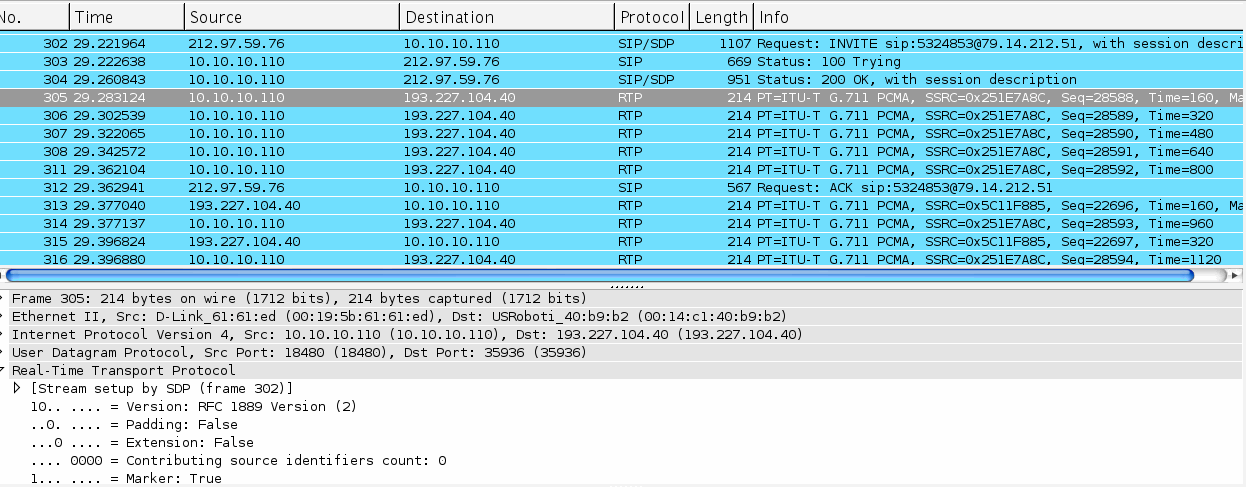
Now start the voice streaming: in this figure this traffic “sniffed” and showed using wireshark.
PBX → ITSP
10.10.10.110 – src port 1840 → 193.227.104.40 dst port 35936
ITSP → PBX
193.227.104.40 src port 35936 → 10.10.10.110 – dst port 1840
We can see that Asterisk start to send packet: in this mode the NAT open the port correctly and the ITSP can reach the Asterisk PBX inside the LAN.
Another very interesting things is that tha ITSP UA use a different Ip Address for the SIP messages and for the RTP stream.
Antother Real Case: Interconnection Asterisk<->Avaya/Nortel BCM 450
In this case an external connected to an Avaya Pbx BCM450 call using SIP an Asterisk PBX.
Asterisk PBX – IP 10.10.10.110
Avaya PBX – IP 10.10.10.155
Extent connected to Avaya PBX that establish the call – IP 10.10.10.87
>> From Avaya to Asterisk
INVITE sip:420;phone-context=subscriber.private@10.10.10.110:5060;transport=udp;user=phone SIP/2.0 From: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=34e03fa8-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-5708f3a4-59a To: <sip:420;phone-context=subscriber.private@10.10.10.110;user=phone> Call-ID: 35036840-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-3609da9e-59a CSeq: 1 INVITE Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.10.10.155:5060;branch=z9hG4bK-59a-15e419-1faa1b5d Max-Forwards: 70 Supported: sipvc,x-nortel-sipvc,100rel,replaces User-Agent: Nortel Networks BCM VoIP Gateway release_46 version_46.46.0.33 P-Asserted-Identity: <sip:anonymous@10.10.10.155> Privacy: id;user x-nt-corr-id: 35036840-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-3609da9e-59a Contact: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid:5060;maddr=10.10.10.155;transport=udp> Allow: INVITE,INFO,ACK,OPTIONS,CANCEL,BYE,NOTIFY,PRACK,UPDATE,REFER Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 334 v=0 o=- 1323100317 1323100317 IN IP4 10.10.10.155 s=- c=IN IP4 10.10.10.87 t=0 0 a=sqn:0 a=cdsc:1 image udptl t38 m=audio 51000 RTP/AVP 18 4 0 8 120 111 c=IN IP4 10.10.10.87 a=fmtp:18 annexb=yes a=fmtp:4 annexa=yes a=rtpmap:120 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:120 0-15 a=rtpmap:111 X-nt-inforeq/8000 a=ptime:30 a=sendrecv
Asterisk -> Avaya
SIP/2.0 100 Trying Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.10.10.155:5060;branch=z9hG4bK-59a-15e419-1faa1b5d;received=10.10.10.155 From: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=34e03fa8-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-5708f3a4-59a To: <sip:420;phone-context=subscriber.private@10.10.10.110;user=phone> Call-ID: 35036840-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-3609da9e-59a CSeq: 1 INVITE User-Agent: FPBX-2.8.1(1.4.40) Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO Supported: replaces Contact: <sip:420@10.10.10.110> Content-Length: 0
From Asterisk to Avaya
SIP/2.0 200 OK Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.10.10.155:5060;branch=z9hG4bK-59a-15e419-1faa1b5d;received=10.10.10.155 From: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=34e03fa8-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-5708f3a4-59a To: <sip:420;phone-context=subscriber.private@10.10.10.110;user=phone>;tag=as5b7d8e50 Call-ID: 35036840-a0a0a9b-13c4-55013-59a-3609da9e-59a CSeq: 1 INVITE User-Agent: FPBX-2.8.1(1.4.40) Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO Supported: replaces Contact: <sip:420@10.10.10.110> Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 206 v=0 o=root 2756 2756 IN IP4 10.10.10.110 s=session c=IN IP4 10.10.10.110 t=0 0 m=audio 16316 RTP/AVP 0 8 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=silenceSupp:off - - - - a=ptime:20 a=sendrecv
It is possible to verify with this Sip packet that the BCM 450 does not behave like a B2BUA: the asterisk pbx & extent of Avaya/Nortel BCM 450 connect itself each other directly !
PREVIOUS POST: From Sip to RTP (Part 5) – Trunks & surroundings
Linkografia
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3325.txt
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol